1. LangChain & LangGraph Cheat Sheet
- 1. LangChain & LangGraph Cheat Sheet
- 1.1 Quick Start (LCEL minimal chain)
- 1.2 Important Links
- 1.3 Getting Started
- 1.4 Core LangChain Components
- 1.5 Prompt Templates (String, Chat, Few-Shot)
- 1.6 LCEL (LangChain Expression Language)
- 1.7 Output Parsers (Pydantic, JSON, Structured)
- 1.8 Memory Systems
- 1.9 Agents & Tools
- 1.10 Agent Execution (loops, errors)
- 1.11 RAG - Retrieval Augmented Generation
- 1.12 Vector Stores (FAISS, Chroma, Pinecone, Weaviate)
- 1.13 Document Processing (Loaders, Splitters)
- 1.14 Embeddings (OpenAI, HF, Cohere, local)
- 1.15 LangGraph Basics (state)
- 1.16 LangGraph Construction (nodes/edges)
- 1.17 LangGraph Execution (invoke, stream, checkpoint)
- 1.18 Conditional Routing
- 1.19 Multi-Agent Patterns
- 1.20 Human-in-the-Loop
- 1.21 Serving & Deployment (LangServe + FastAPI)
- 1.22 Production Deployment (Docker, scaling)
- 1.23 LangSmith Monitoring
- 1.24 Caching & Optimization
- 1.25 RAG with LCEL (Modern Pattern)
- 1.26 Conversational RAG
- 1.27 Structured Output with Pydantic
- 1.28 Async Operations
- 1.29 Error Handling & Retries
- 1.30 Multi-Query Retrieval
- 1.31 Hybrid Retrieval (Dense + Sparse)
- 1.32 Contextual Compression
- 1.33 Streaming Responses
- 1.34 Function/Tool Calling
- 1.35 Batch Processing
- 1.36 Advanced Patterns (Reflection, ReAct, tools in graphs)
- 1.37 Best Practices
This cheat sheet provides a deep, end-to-end reference for LangChain and LangGraph: core components, LCEL, memory, agents, RAG, embeddings, graph construction, routing, serving/deployment, and monitoring. Each concept is shown with a concise explanation, ASCII/Unicode box-drawing diagram, practical code, and actionable tips.
1.1 Quick Start (LCEL minimal chain)
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are concise."),
("user", "Question: {question}")
])
chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
print(chain.invoke({"question": "What is LangChain?"}))
1.2 Important Links
- LangChain Python Docs: https://python.langchain.com
- LangGraph Docs: https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/
- LangServe Docs: https://python.langchain.com/docs/langserve
- LangSmith Docs: https://docs.smith.langchain.com
- LCEL Guide: https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/
1.3 Getting Started
Brief: Install core packages, set API keys, and verify environment.
Diagram:
┌──────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ Install │→→→│ Configure │→→→│ Validate │
│ langchain │ │ API Keys │ │ imports │
└──────────────┘ └──────┬──────┘ └──────┬──────┘
│ │
↓ ↓
┌────────────────┐ ┌────────────┐
│ OPENAI_API_KEY │ │ python -c │
│ HUGGINGFACE_* │ │ "import │
└────────────────┘ │ langchain"│
└────────────┘
Code:
pip install "langchain>=0.3" "langgraph>=0.2" langchain-openai langchain-community langchain-core
# Optional extras: vector stores, parsers, serving
pip install faiss-cpu chromadb pinecone-client weaviate-client pydantic openai fastapi uvicorn redis
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-..."
# Optional: LangSmith for tracing
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_API_KEY"] = "ls_..."
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_ENDPOINT"] = "https://api.smith.langchain.com"
Tips: - Keep secrets in env vars or .env + python-dotenv. - Pin versions for reproducibility (pip freeze > requirements.txt). - Verify GPU/CPU availability before large embeddings.
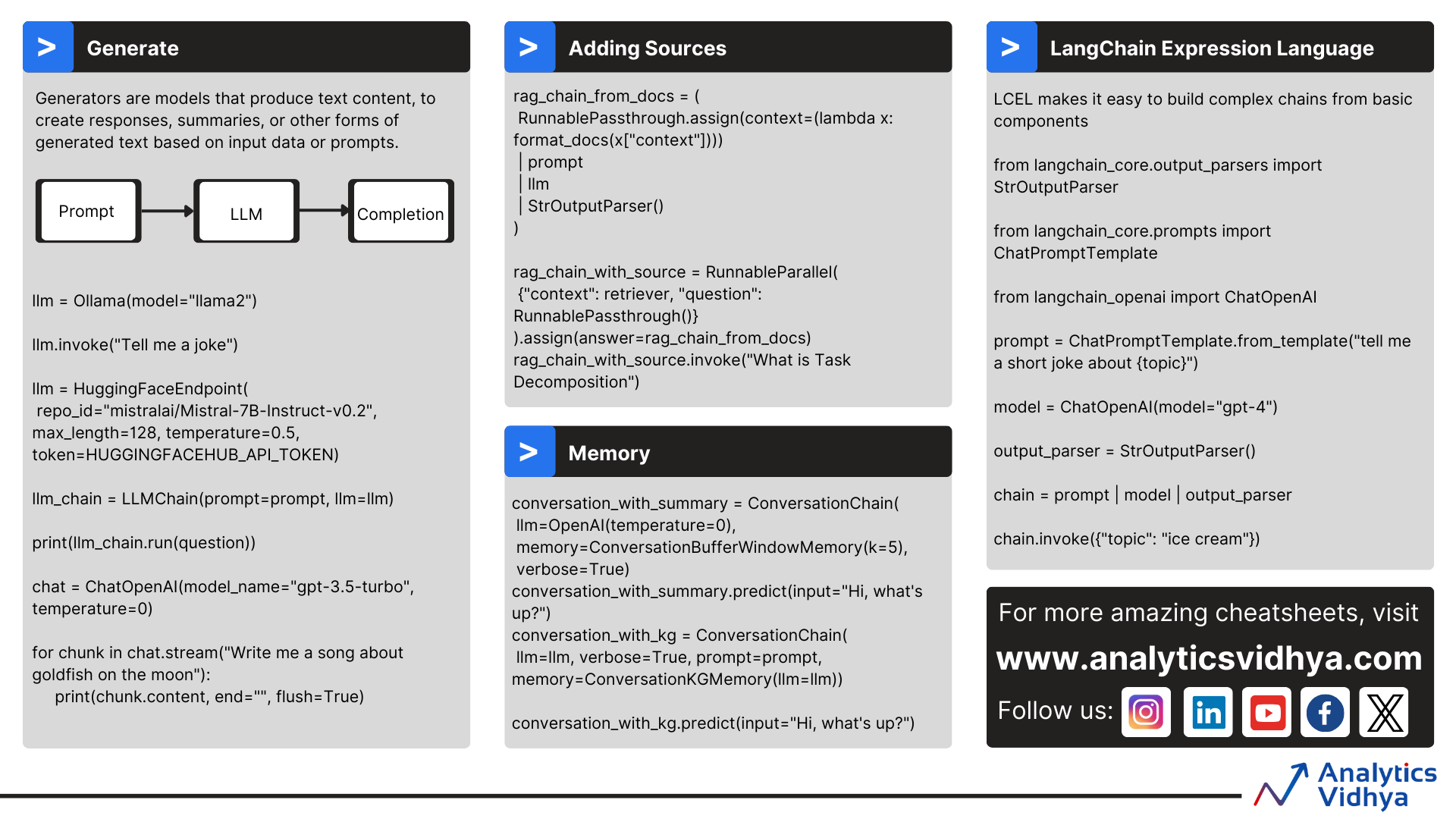
1.4 Core LangChain Components
Brief: Models (LLMs vs Chat), Prompts, Output Parsers, Chains.
Diagram:
┌─────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌─────────┐
│ Input │ → │ Prompt │ → │ Model (LLM/ │ → │ Parser │
│ (user) │ │ Template │ │ ChatModel) │ │ (struct)│
└─────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────┬───────┘ └────┬────┘
│ │
↓ ↓
┌────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ Chain │ → │ Output │
└────────┘ └──────────┘
Code:
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are concise."),
("user", "Question: {question}")
])
chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
print(chain.invoke({"question": "What is LangChain?"}))
Tips: - Use temperature=0 for deterministic outputs; higher for creativity. - Always parse outputs for downstream safety (JSON, Pydantic, etc.). - Prefer Chat models for function/tool calling.
1.5 Prompt Templates (String, Chat, Few-Shot)
Brief: Parameterized prompts to control style and context.
Diagram:
┌─────────────┐ variables ┌─────────────────┐
│ Base Prompt │ ───────────→ │ Rendered Prompt │
└─────┬───────┘ └────────┬────────┘
│ few-shot examples │ to model
↓ ↓
┌─────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐
│ Example 1 │ │ Chat Messages │
├─────────────┤ └───────────────┘
│ Example 2 │
└─────────────┘
Code:
from langchain_core.prompts import (PromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate,
FewShotPromptTemplate)
string_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template("Translate to French: {text}")
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a translator."),
("user", "Translate: {text}")
])
examples = [
{"text": "hello", "translation": "bonjour"},
{"text": "good night", "translation": "bonne nuit"},
]
example_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template("Input: {text}\nOutput: {translation}")
few_shot = FewShotPromptTemplate(
examples=examples,
example_prompt=example_prompt,
prefix="Use examples to guide style.",
suffix="Input: {text}\nOutput:",
input_variables=["text"],
)
print(few_shot.format(text="thank you"))
Tips: - Keep examples short; match target style. - Use placeholders consistently; validate with prompt.format(). - For chat, keep system message focused; add guardrails.
1.6 LCEL (LangChain Expression Language)
Brief: Compose chains with |, parallel branches, passthrough, streaming, async.
Diagram (LCEL Pipe Flow):
Input
│
├─→ ┌──────────┐ → ┌────────────┐ → ┌──────────────┐ → Output
│ │ Transform │ │ Transform │ │ Transform │
│ └──────────┘ └────────────┘ └──────────────┘
│
└─→ ┌───────────────┐
│ RunnableParallel│ (fan-out, then merge)
└───────────────┘
Code:
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableParallel, RunnablePassthrough
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Summarize and extract keywords."),
("user", "{text}")
])
branch = RunnableParallel(
summary=prompt | llm | StrOutputParser(),
keywords=prompt | llm | StrOutputParser(),
)
chain = RunnablePassthrough.assign(text=lambda x: x["text"]) | branch
result = chain.invoke({"text": "LangChain simplifies LLM orchestration."})
print(result)
Tips: - Use assign to enrich inputs without losing originals. - astream()/astream_events() for streaming tokens/events. - Compose sync/async seamlessly; prefer async for I/O-heavy pipelines.
1.7 Output Parsers (Pydantic, JSON, Structured)
Brief: Enforce structured outputs for safety and determinism.
Diagram:
┌───────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐
│ LLM Text │ → │ OutputParser │ → │ Typed Object │
└───────────┘ └──────┬───────┘ └────────┬───────┘
│ jsonschema │ pydantic
↓ ↓
┌─────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐
│ Validation │ │ raise errors │
└─────────────┘ └──────────────┘
Code:
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
class Answer(BaseModel):
summary: str = Field(..., description="Brief answer")
sources: list[str]
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Answer)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Return JSON matching the schema."),
("user", "Question: {question}\n{format_instructions}")
]).partial(format_instructions=parser.get_format_instructions())
chain = prompt | llm | parser
print(chain.invoke({"question": "What is LangGraph?"}))
Tips: - Use OutputFixingParser to auto-correct near-misses. - Prefer StructuredOutputParser/PydanticOutputParser for reliability. - Validate early before persisting to DBs.
1.8 Memory Systems
Brief: Store conversational context: buffer, summary, windowed, vector, entity-aware.
Diagram (Memory Types Comparison):
┌───────────────┬───────────────────────┬──────────────────────────┐
│ Type │ Pros │ Cons │
├───────────────┼───────────────────────┼──────────────────────────┤
│ Buffer │ Exact history │ Grows unbounded │
│ BufferWindow │ Recent k messages │ Loses older context │
│ Summary │ Compressed narrative │ Possible detail loss │
│ VectorStore │ Semantic recall │ Needs embeddings/store │
│ EntityMemory │ Tracks entities slots │ Setup complexity │
└───────────────┴───────────────────────┴──────────────────────────┘
Code:
from langchain.memory import (ConversationBufferMemory,
ConversationBufferWindowMemory, ConversationSummaryMemory,
ConversationEntityMemory)
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
buffer = ConversationBufferMemory(return_messages=True)
window = ConversationBufferWindowMemory(k=3, return_messages=True)
summary = ConversationSummaryMemory(llm=llm, return_messages=True)
entity = ConversationEntityMemory(llm=llm)
# Vector store memory
embedding = OpenAIEmbeddings()
vs = FAISS.from_texts(["Hello world"], embedding)
Tips: - Pick memory based on cost vs fidelity: window for short chats; summary for long. - Vector memory helps retrieve semantic context; tune chunk size/overlap. - Clear memory per session to avoid leakage across users.
1.9 Agents & Tools
Brief: Agents choose tools dynamically; tools expose functions.
Diagram (Agent Decision Loop):
┌─────────────────┐
│ Start Agent │
└────────┬────────┘
↓
┌────────────────────────────────┐
│ OBSERVE │
│ - User query │
│ - Previous tool outputs │
│ - Current state │
└────────┬───────────────────────┘
↓
┌────────────────────────────────┐
│ THINK (LLM Reasoning) │
│ - Analyze observation │
│ - Review available tools │
│ - Plan next action │
└────────┬───────────────────────┘
↓
┌────────────────────┐
│ DECIDE │
└────────┬───────────┘
│
┌────────────────┼────────────────┐
↓ ↓ ↓
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ Use Tool A │ │ Use Tool B │ │ Final Answer│
└─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘
↓
┌────────────────────┐
│ ACT │
└────────────────────┘
Diagram (Agent with Multiple Tools):
┌──────────────┐
│ Agent Brain │
└──────┬───────┘
↓
┌───────┬───────────┬───────────┬───────────┐
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
┌──────┐ ┌───────┐ ┌────────┐ ┌────────┐ ┌─────────┐
│Search│ │Calc │ │Weather │ │Custom │ │Feedback │
│API │ │Tool │ │Tool │ │Tool │ │Loop │
└──┬───┘ └──┬─────┘ └──┬────┘ └──┬────┘ └────┬─────┘
│ │ │ │ │
└────────┴───────────┴─────────┴────────────┘
↑ aggregated observation
Diagram (Agent Type Selection Tree):
┌───────────────────────┐
│ Need structured tools?│
└───────────┬───────────┘
│Yes
↓
┌─────────────┐
│ Tool-Calling│ (OpenAI-style)
└────┬────────┘
│No
↓
┌────────────────────────┐
│ Dialogue heavy? │
└─────────┬──────────────┘
│Yes │No
↓ ↓
┌────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────┐
│ Conversational │ │ Zero-Shot ReAct │
│ Agent │ │ (plan & act inline) │
└────────────────┘ └─────────┬───────────┘
│ Need long plans?
↓
┌──────────────┐
│ Plan-and-Exec│
└──────────────┘
Code:
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_tool_calling_agent
from langchain.tools import tool
@tool
def multiply(a: float, b: float) -> float:
"""Multiply two numbers."""
return a * b
llm_tools = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Use tools when helpful."),
("user", "{input}")
])
agent = create_tool_calling_agent(llm_tools, [multiply], prompt)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=[multiply], verbose=True)
print(agent_executor.invoke({"input": "What is 12*9?"}))
Tips: - Keep tool signatures small, well-described docstrings. - Return structured JSON to simplify parsing. - Add guardrails (e.g., tool whitelists, max iterations).
1.10 Agent Execution (loops, errors)
Brief: AgentExecutor orchestrates reasoning, tool calls, retries.
Diagram:
┌──────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ User In │→→│ Agent Executor│→→│ Tool Calls │→→│ Final Out │
└────┬─────┘ └──────┬───────┘ └──────┬───────┘ └────┬─────┘
│ retry/backoff │ errors │ streaming tokens │
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
Logs/Traces Error Handler Partial Results Return
Code:
result = agent_executor.invoke({"input": "Plan weekend: check weather in NYC and suggest indoor/outdoor."})
# For streaming thoughts
for event in agent_executor.astream_events({"input": "..."}):
print(event)
Tips: - Set handle_parsing_errors=True or custom handler for robust runs. - Cap max_iterations; log intermediate steps. - Include tool observation snippets in prompts to avoid loops.
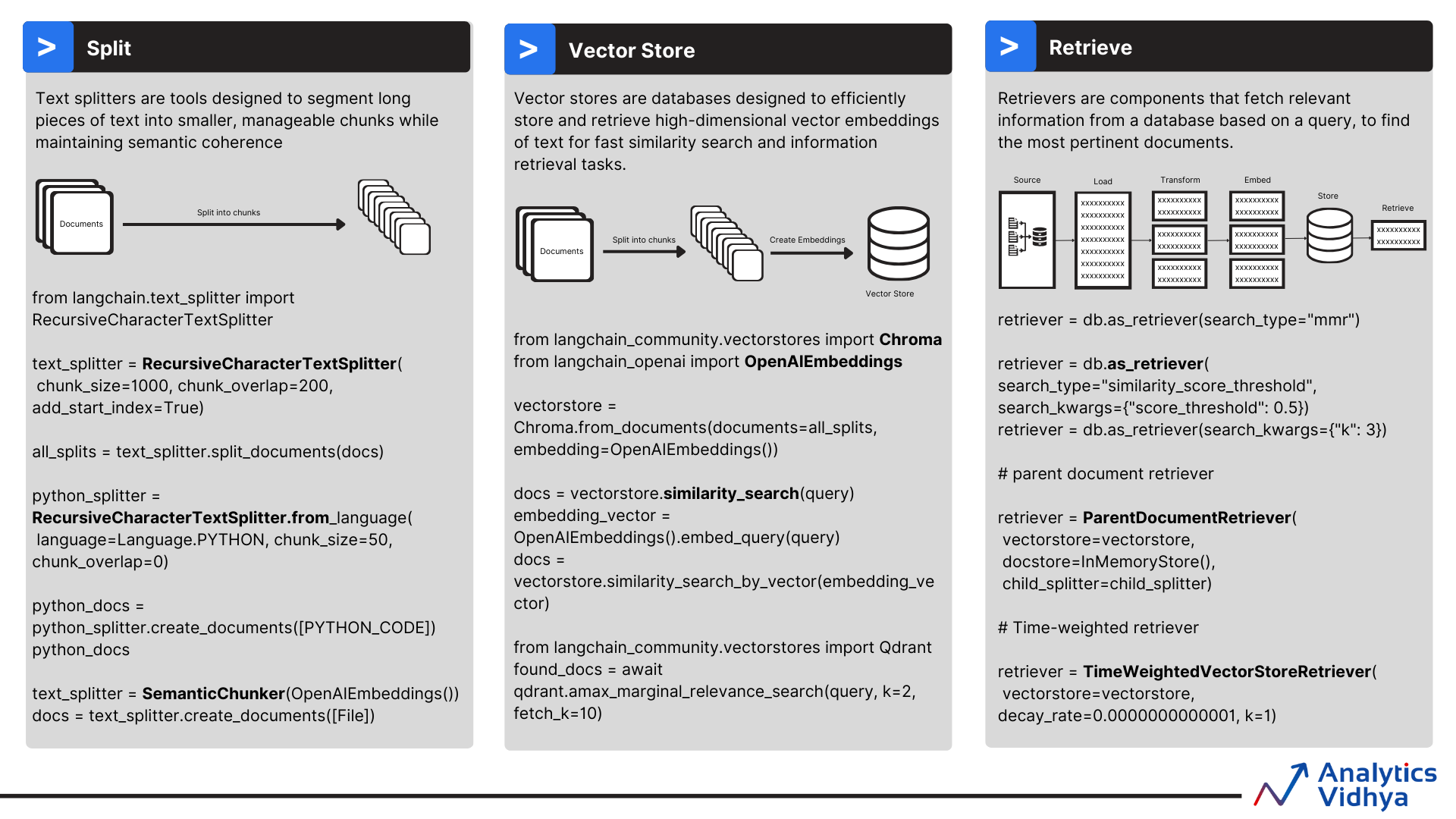
1.11 RAG - Retrieval Augmented Generation
Brief: Retrieve relevant chunks then generate grounded answers.
Diagram (RAG Full Pipeline):
┌────────────┐ ┌───────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌────────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ Document │ → │ Loaders │ → │ Splitter │ → │ Embeddings │ → │ Vector DB│
│ Store/FS │ │ (PDF/URL) │ │ chunks │ │ (OpenAI/ │ │ (FAISS/ │
└─────┬──────┘ └────┬──────┘ └────┬─────┘ │ HF/Cohere) │ │ Chroma…) │
│ │ │ └────┬──────┘ └────┬─────┘
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ ↓ ↓
│ │ │ ┌────────────┐ ┌────────────┐
│ Query │ │ │ Similarity │ │ Retrieved │
└───────────────┴─────────────┴──────→ │ Search │→ │ Chunks │
└────┬───────┘ └────┬──────┘
↓ ↓
┌──────────────────────────┐
│ LLM (prompt with context)│
└──────────────────────────┘
Diagram (RAG Chain Types Table):
┌────────────┬───────────────┬────────────────────┬──────────────────────┐
│ Strategy │ How │ Pros │ Cons │
├────────────┼───────────────┼────────────────────┼──────────────────────┤
│ Stuff │ Concatenate │ Simple, fast │ Context length bound │
│ Map-Reduce │ Map chunks -> │ Scales, summaries │ More LLM calls │
│ │ partial, then │ │ │
│ │ reduce │ │ │
│ Refine │ Iterative add │ Keeps detail │ Sequential latency │
│ Map-Rerank │ Score each │ Better precision │ Costly reranking │
└────────────┴───────────────┴────────────────────┴──────────────────────┘
Code:
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
loader = WebBaseLoader("https://python.langchain.com")
docs = loader.load()
splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=800, chunk_overlap=120)
chunks = splitter.split_documents(docs)
emb = OpenAIEmbeddings()
vectorstore = FAISS.from_documents(chunks, emb)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_type="similarity", search_kwargs={"k": 4})
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=llm,
chain_type="map_reduce", # or "stuff", "refine", "map_rerank"
retriever=retriever,
)
print(qa_chain.invoke({"query": "How does LCEL work?"}))
Tips: - Tune chunk_size to ~200-1000 tokens; overlap ~10-20%. - Choose chain type per corpus size: stuff for small, map_reduce for large. - Add citations by returning source metadata in prompt.
1.12 Vector Stores (FAISS, Chroma, Pinecone, Weaviate)
Brief: Persistent similarity search backends.
Diagram:
┌────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ Text/Chunk │→→│ Embeddings │→→│ Vector Store │
└────┬───────┘ └──────┬──────┘ └──────┬──────┘
│ │ │
↓ ↓ ↓
Query Text → embed → similarity search → Top-k IDs → Fetch docs
Code:
# FAISS (local)
faiss_store = FAISS.from_documents(chunks, emb)
faiss_store.save_local("faiss_index")
faiss_loaded = FAISS.load_local("faiss_index", emb, allow_dangerous_deserialization=True)
# Chroma (local serverless)
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
chroma = Chroma.from_documents(chunks, emb, collection_name="docs")
# Pinecone (managed)
import pinecone
pinecone.Pinecone(api_key="...")
from langchain.vectorstores import Pinecone as PineconeVS
pinecone_index = pinecone.Index("langchain-demo")
pinecone_vs = PineconeVS(index=pinecone_index, embedding_function=emb.embed_query)
# Weaviate (managed/self-hosted)
import weaviate
client = weaviate.Client("https://xyz.weaviate.network", auth_client_secret=weaviate.AuthApiKey("..."))
Tips: - Pick HNSW (Chroma/Weaviate) for fast recall; IVF/Flat in FAISS for precision. - Normalize vectors for cosine similarity when required. - Persist indexes; align embedding model at query and ingest time.
1.13 Document Processing (Loaders, Splitters)
Brief: Load diverse sources and split text for retrieval.
Diagram (Text Splitter Strategies):
┌──────────────┬───────────────────────────┬──────────────────────────┐
│ Strategy │ How │ Best For │
├──────────────┼───────────────────────────┼──────────────────────────┤
│ Character │ Fixed chars + overlap │ Clean text │
│ Recursive │ Fallback by delimiters │ Mixed formats │
│ Token-based │ Token counts (tiktoken) │ Token budgets │
│ Semantic │ Embedding-based merge │ Coherent chunks │
└──────────────┴───────────────────────────┴──────────────────────────┘
Code:
from langchain_community.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader, CSVLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import (CharacterTextSplitter,
RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter, TokenTextSplitter)
pdf_docs = PyPDFLoader("file.pdf").load()
csv_docs = CSVLoader("data.csv").load()
rec_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=80)
chunks = rec_splitter.split_documents(pdf_docs + csv_docs)
Tips: - Strip headers/footers before splitting PDFs when possible. - Use TokenTextSplitter for strict token budgets. - Preserve metadata (page, URL) for citations.
1.14 Embeddings (OpenAI, HF, Cohere, local)
Brief: Convert text to vectors for similarity search.
Diagram:
┌──────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐
│ Raw Text │→→│ Embed Model │→→│ Vector (dims) │
└──────────┘ └──────┬───────┘ └──────┬───────┘
│ norm │ store/reuse
↓ ↓
Cache/DB Retrieval pipelines
Code:
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_community.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings, CohereEmbeddings
openai_emb = OpenAIEmbeddings(model="text-embedding-3-small")
hf_emb = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
cohere_emb = CohereEmbeddings(model="embed-english-light-v3.0", cohere_api_key="...")
Tips: - Match embedding model language/domain to corpus. - Batch embeddings to reduce latency; cache results. - For local privacy, prefer HF or GGUF-based models.
1.15 LangGraph Basics (state)
Brief: Build graphs where nodes are steps; state carried via typed dicts/reducers.
Diagram (StateGraph Execution):
┌────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌────────┐
│ START │ → │ Node A │ → │ Node B │ → │ END │
└────────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────────┘
│ │
└─────→──────┘ (conditional edge)
Diagram (State Reducer Behavior):
With reducer (operator.add): Without reducer:
┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ state=1 │ → │ add 2 │ = 3 │ state=1 │ → │ set 2 │ = 2
└──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘
Code:
from typing import TypedDict, Annotated
from operator import add
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
class GraphState(TypedDict):
message: str
steps: Annotated[list[str], add] # reducer concatenates lists
graph = StateGraph(GraphState)
def start(state: GraphState):
return {"message": state["message"], "steps": ["start"]}
def finish(state: GraphState):
return {"message": state["message"], "steps": state["steps"] + ["finish"]}
graph.add_node("start", start)
graph.add_node("finish", finish)
graph.add_edge("start", "finish")
graph.set_entry_point("start")
graph.set_finish_point("finish")
compiled = graph.compile()
print(compiled.invoke({"message": "hi", "steps": []}))
Tips: - Use reducers (e.g., operator.add) for accumulating lists/counters safely. - TypedDict enforces state shape; fail fast on missing keys. - Prefer pure functions for nodes; keep side-effects minimal.
1.16 LangGraph Construction (nodes/edges)
Brief: Build graphs with nodes, edges, conditionals.
Code:
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
g = StateGraph(GraphState)
g.add_node("decide", lambda s: {"route": "a" if "math" in s["message"] else "b"})
g.add_node("tool_a", lambda s: {"result": "used A"})
g.add_node("tool_b", lambda s: {"result": "used B"})
# Conditional routing
from langgraph.graph import add_conditional_edges
add_conditional_edges(
g,
source="decide",
path_map={"a": "tool_a", "b": "tool_b"},
)
g.add_edge("tool_a", END)
g.add_edge("tool_b", END)
g.set_entry_point("decide")
compiled = g.compile()
print(compiled.invoke({"message": "math question", "steps": []}))
Tips: - Always set entry + finish points. - Use add_conditional_edges for clean branching logic. - Keep node names descriptive; log transitions for debugging.
1.17 LangGraph Execution (invoke, stream, checkpoint)
Brief: Run graphs sync/async with streaming and persistence.
Diagram:
┌────────┐ invoke() ┌──────────┐ stream tokens ┌────────────┐
│ Client │────────────→│ Graph │────────────────→ │ Responses │
└────────┘ └──────────┘ └────────────┘
│ checkpoint
└────────────→ storage (Redis/S3/DB)
Code:
compiled = graph.compile(checkpointer=None) # or Redis/S3 checkpointer
# Single call
compiled.invoke({"message": "hi", "steps": []})
# Streaming
for event in compiled.astream_events({"message": "hi", "steps": []}):
print(event)
# Checkpointing with Redis (resume later)
from langgraph.checkpoint.redis import RedisCheckpointSaver
import redis
r = redis.Redis(host="localhost", port=6379, db=0)
checkpointer = RedisCheckpointSaver(r)
compiled_ckpt = graph.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)
run = compiled_ckpt.invoke({"message": "hi", "steps": []})
# ... later
compiled_ckpt.resume(run["checkpoint_id"])
Tips: - Use a checkpointer (e.g., Redis) for resumable flows. - Prefer streaming for chat UX; buffer for batch jobs. - Persist state for human handoffs or crash recovery.
1.18 Conditional Routing
Brief: Route based on state values or model decisions.
Diagram:
┌────────┐ ┌────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐
│ Input │→→│ Router Node │→→│ Branch A │
└────────┘ └────┬───────┘ └─────┬────────┘
│ │
↓ ↓
┌────────────────────────────┐
│ Branch B │
└────────────────────────────┘
Code:
def router(state):
if "finance" in state["message"]:
return "finance"
return "general"
add_conditional_edges(g, "decide", {"finance": "tool_b", "general": "tool_a"})
Tips: - Keep routing functions pure and deterministic when possible. - For LLM-based routing, constrain outputs (JSON labels) and validate. - Add default fallbacks to avoid dead ends.
1.19 Multi-Agent Patterns
Brief: Supervisor coordinates specialist agents.
Diagram (Multi-Agent Supervisor):
┌──────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐
│User │→→│ Supervisor │→→│ Task Decompose│
└──┬───┘ └──────┬──────┘ └──────┬───────┘
│ │ │
↓ ↓ ↓
┌────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│Research│ │Writer │ │FactChecker │ │CodeRunner │
└────┬───┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬──────┘ └────┬────────┘
│ │ │ │
└──────────┴─────→─────────┴────→────────────┘
Aggregation → Final Answer
Code:
# Pseudocode skeleton
supervisor = compiled # a LangGraph coordinating agents
# Each specialist is a tool-calling chain; supervisor routes tasks
Tips: - Give each agent narrow scope + tools; supervisor merges. - Prevent loops with max hops/iterations. - Log per-agent traces for debugging.
1.20 Human-in-the-Loop
Brief: Interrupt, review, then resume with checkpoints.
Diagram (Human-in-the-Loop Flow):
┌─────────────┐ ┌───────────┐ ┌───────────┐ ┌───────────┐
│ Execute │→→│ Checkpoint │→→│ Interrupt │→→│ Human OK? │
└─────┬───────┘ └────┬──────┘ └────┬──────┘ └────┬──────┘
│ │ │ │Yes │No
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
Resume ←────────── Save Review Reject/Amend
Code:
# Use a checkpointer; pause on specific node
state = compiled.invoke(...)
# Later, resume with stored checkpoint id
compiled.resume(checkpoint_id="abc123")
Tips: - Define explicit pause points (e.g., before external actions). - Store human feedback in state for auditability. - Timebox approvals to avoid stale sessions.
1.21 Serving & Deployment (LangServe + FastAPI)
Brief: Expose chains/graphs as REST endpoints.
Diagram (LangServe Deployment):
Client → API Gateway → LangServe (FastAPI) → Chain/Graph → Response
Code (LangServe):
# app.py
from fastapi import FastAPI
from langserve import add_routes
from my_chains import chain, graph
app = FastAPI()
add_routes(app, chain, path="/chain")
add_routes(app, graph, path="/graph")
# Run
# uvicorn app:app --reload --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
Add Authentication:
# Simple API key guard
API_KEY = "changeme"
@app.middleware("http")
async def auth(request: Request, call_next):
if request.headers.get("x-api-key") != API_KEY:
raise HTTPException(status_code=401, detail="Unauthorized")
return await call_next(request)
Test/Call with curl:
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8000/chain/invoke" \
-H "x-api-key: changeme" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"input": {"question": "Hello"}}'
Tips: - Validate request schemas; limit concurrency via worker settings. - Use uvicorn --workers for CPU-bound or async I/O. - Add auth (API keys/JWT) at gateway or FastAPI middleware.
1.22 Production Deployment (Docker, scaling)
Brief: Containerize, scale horizontally, add caching and observability.
Diagram (Production Architecture):
┌──────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐ ┌───────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ Clients │→→│ Load Balancer │→→│ App Pods │→→│ Vector DB │
└──────────────┘ └──────┬────────┘ └────┬──────┘ └────┬─────┘
│ │ │
↓ ↓ ↓
┌────────┐ ┌─────────┐ ┌─────────┐
│ Redis │ │ Postgres│ │ Metrics │
│ Cache │ │ /S3 │ │+Tracing │
└────────┘ └─────────┘ └─────────┘
Code (Dockerfile snippet):
FROM python:3.11-slim
WORKDIR /app
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
COPY . .
CMD ["uvicorn", "app:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "8000"]
Tips: - Externalize secrets via env vars/secret managers. - Use autoscaling on CPU/RAM/QPS; warm LLM connections. - Add health probes (/healthz) and readiness checks.
Docker Compose (app + chroma + prometheus minimal):
services:
app:
build: .
environment:
- OPENAI_API_KEY=${OPENAI_API_KEY}
ports: ["8000:8000"]
depends_on: [chroma]
chroma:
image: ghcr.io/chroma-core/chroma:latest
ports: ["8001:8000"]
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus:latest
ports: ["9090:9090"]
1.23 LangSmith Monitoring
Brief: Trace, debug, and evaluate chains/agents.
Diagram:
┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌────────────┐
│ Chains │→→│ Tracer │→→│ LangSmith UI │→→│ Insights │
└────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────────┘ └────┬───────┘
│ logs/errors │ spans │ filters │ actions
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
Storage Timing/Cost Compare runs Prompt fixes
Code:
import os
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2"] = "true"
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_PROJECT"] = "my-app"
# Traces auto-captured when using langchain core runtimes
Tips: - Tag runs with metadata (user id, version) for filtering. - Use datasets + evals to compare prompt/model changes. - Inspect tool call errors to tighten parsing.
1.24 Caching & Optimization
Brief: Reduce latency/cost via caching and prompt/model choices.
Diagram:
┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ Request │→→│ Cache? │→→│ Response │
└────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘
│ miss │ hit │
↓ ↓ ↓
Call LLM Return cached Store result
Code:
from langchain.cache import SQLiteCache
from langchain.globals import set_llm_cache
set_llm_cache(SQLiteCache(database_path=".langchain_cache.sqlite"))
Tips: - Cache deterministic calls (temperature 0) keyed on prompt+input. - Use shorter prompts, smaller models (gpt-4o-mini, gpt-3.5-turbo) for bulk. - Batch embeddings; reuse vector store across sessions.
Cost/Latency quick picks:
┌────────────┬─────────────────────────────┬────────────────────┐
│ Use Case │ Model/Setting │ Why │
├────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼────────────────────┤
│ Cheap bulk │ gpt-3.5-turbo, temp 0 │ Low cost, fast │
│ Quality │ gpt-4o-mini, temp 0.2 │ Balance quality │
│ Max quality│ gpt-4o, temp 0-0.3 │ Best reasoning │
│ RAG ingest │ chunk 500-800, overlap 10% │ Good recall/size │
│ Caching │ Redis/SQLite, key prompt+in │ Cut repeat costs │
└────────────┴─────────────────────────────┴────────────────────┘
Testing prompts/parsers (pytest sketch):
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
def test_prompt_format():
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Be short."),
("user", "{q}")
])
rendered = prompt.format(q="hi")
assert "hi" in rendered
def test_parser_deterministic(monkeypatch):
parser = StrOutputParser()
# Mock LLM call
class FakeLLM:
def invoke(self, *_args, **_kwargs):
return "ok"
chain = FakeLLM() | parser # type: ignore
assert chain.invoke({}) == "ok"
1.25 RAG with LCEL (Modern Pattern)
Brief: Build RAG pipelines using LCEL pipe operator for clean composition.
Diagram:
┌──────────┐ ┌───────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ Question │→→│ Retriever │→→│ Retrieved │→→│ Prompt │→→│ LLM │
│ │ │ (vector) │ │ Context │ │ + Ctx │ │ Answer │
└──────────┘ └───────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────┘ └──────────┘
↑ ↓
│ similarity search │
┌──────────────┐ ┌───────────┐
│ Vector Store │ │ Parsed │
│ (embeddings) │ │ Response │
└──────────────┘ └───────────┘
Code:
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
# Setup
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
vectorstore = FAISS.from_texts(
["LangChain simplifies LLM apps", "LCEL enables composition"],
embeddings
)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 2})
# Build RAG chain with LCEL
template = """Answer based on context:
Context: {context}
Question: {question}
Answer:"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
rag_chain = (
{"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
| prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
# Use
answer = rag_chain.invoke("What is LangChain?")
Tips: - Use RunnablePassthrough() to preserve input in parallel branches - Chain components with | for readable pipelines - Add .with_config({"run_name": "rag"}) for better tracing
1.26 Conversational RAG
Brief: RAG with conversation history for follow-up questions.
Diagram:
┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐ ┌───────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ New Question │→→│ + Chat History │→→│ Retriever │→→│ Context │
└──────────────┘ └────────┬─────────┘ └───────────┘ └────┬─────┘
│ │
↓ ↓
┌─────────────────┐ ┌────────────────────┐
│ Reformulated │ │ Answer with │
│ Question │──────────────→│ Context + History │
└─────────────────┘ └────────────────────┘
↑ │
│ ↓
┌─────────────────┐ ┌────────────────────┐
│ History Buffer │←─────────────│ Update History │
│ (last N turns) │ └────────────────────┘
└─────────────────┘
Code:
from langchain.chains import create_history_aware_retriever, create_retrieval_chain
from langchain.chains.combine_documents import create_stuff_documents_chain
from langchain_core.prompts import MessagesPlaceholder
# Contextualize question based on chat history
contextualize_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Reformulate question using chat history."),
MessagesPlaceholder("chat_history"),
("human", "{input}"),
])
history_aware_retriever = create_history_aware_retriever(
llm, retriever, contextualize_prompt
)
# Answer with retrieved context
qa_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Answer using context:\n{context}"),
MessagesPlaceholder("chat_history"),
("human", "{input}"),
])
qa_chain = create_stuff_documents_chain(llm, qa_prompt)
rag_chain = create_retrieval_chain(history_aware_retriever, qa_chain)
# Use with history
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, AIMessage
chat_history = [
HumanMessage(content="What is LangChain?"),
AIMessage(content="LangChain is a framework for LLM apps."),
]
result = rag_chain.invoke({
"input": "What does it simplify?",
"chat_history": chat_history
})
Tips: - Store chat_history in session/database for multi-turn conversations - Limit history to last 10 messages to control context window - Use ConversationBufferMemory for automatic history management
1.27 Structured Output with Pydantic
Brief: Get typed, validated responses using with_structured_output.
Diagram:
┌──────────┐ ┌────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐
│ Prompt │→→│ LLM │→→│ JSON Schema │→→│ Pydantic │
│ + Schema │ │ (function │ │ Validation │ │ Object │
└──────────┘ │ calling) │ └─────────────┘ └──────┬───────┘
└────────────┘ ↓ │ typed
│ │ ↓
│ ✓ Valid JSON ┌──────────────┐
│ │ │ .name, .age │
│ ✗ Invalid │ .email │
└──────────→ Retry/Error └──────────────┘
Code:
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
class Person(BaseModel):
name: str = Field(description="Person's full name")
age: int = Field(description="Person's age")
email: str = Field(description="Email address")
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(Person)
# Get typed output
person = structured_llm.invoke("Extract info: John Doe, 30 years old, john@example.com")
print(f"{person.name} is {person.age}") # Typed access
# In a chain
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Extract person information from text."),
("human", "{text}")
])
chain = prompt | structured_llm
result = chain.invoke({"text": "Jane Smith, age 25, jane@test.com"})
Tips: - Use Field(description=...) for better extraction accuracy - Works with OpenAI, Anthropic (function calling support required) - Fallback to PydanticOutputParser for models without native support
1.28 Async Operations
Brief: Use async for concurrent operations and better throughput.
Diagram:
Sync (Sequential): Async (Parallel):
┌──────┐ ┌──────────────────────┐
│ Q1 │ 2s │ Q1 │ Q2 │ Q3 │ │
├──────┤ └──┬───┴──┬─┴──┬───────┘
│ Q2 │ 2s Total: 6s ↓ ↓ ↓ Total: 2s
├──────┤ ┌────────────────────┐
│ Q3 │ 2s │ All complete │
└──────┘ └────────────────────┘
asyncio.gather() enables parallel execution:
┌───────────┐ ┌───────────┐ ┌───────────┐
│ ainvoke() │ │ ainvoke() │ │ ainvoke() │
│ Task 1 │ │ Task 2 │ │ Task 3 │
└─────┬─────┘ └─────┬─────┘ └─────┬─────┘
└───────────────┴───────────────┘
│
┌───────▼────────┐
│ await gather() │
└───────┬────────┘
↓
┌────────────────┐
│ All Results │
└────────────────┘
Code:
import asyncio
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI()
# Single async call
async def ask_question():
response = await llm.ainvoke("What is AI?")
return response.content
# Concurrent calls
async def ask_multiple():
questions = ["What is AI?", "What is ML?", "What is NLP?"]
tasks = [llm.ainvoke(q) for q in questions]
responses = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
return [r.content for r in responses]
# Async streaming
async def stream_response():
async for chunk in llm.astream("Explain quantum computing"):
print(chunk.content, end="", flush=True)
# Run async
asyncio.run(ask_multiple())
Tips: - Use ainvoke(), astream(), abatch() for async variants - Combine with asyncio.gather() for parallel LLM calls - Set concurrency limits to avoid rate limiting: asyncio.Semaphore(5)
1.29 Error Handling & Retries
Brief: Handle failures gracefully with retries and fallbacks.
Diagram:
Exponential Backoff: Fallback Chain:
┌────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ Try Call │ │ GPT-4o │
└─────┬──────┘ │ (primary) │
│ └──────┬──────┘
↓ Error │ Error
┌────────────┐ ↓
│ Wait 2^0=1s│ ┌─────────────┐
└─────┬──────┘ │ GPT-4o-mini │
│ │ (fallback) │
↓ Error └──────┬──────┘
┌────────────┐ │ Error
│ Wait 2^1=2s│ ↓
└─────┬──────┘ ┌─────────────┐
│ │ GPT-3.5 │
↓ Error │ (fallback2) │
┌────────────┐ └──────┬──────┘
│ Wait 2^2=4s│ │
└─────┬──────┘ ↓
│ ┌─────────────┐
↓ Success/Fail │ Response or │
┌────────────┐ │ Final Error │
│ Return │ └─────────────┘
└────────────┘
Code:
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableRetry
from langchain.callbacks.manager import CallbackManager
import time
# Retry with exponential backoff
def retry_with_backoff(func, max_retries=3):
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
return func()
except Exception as e:
if attempt == max_retries - 1:
raise
wait_time = 2 ** attempt
print(f"Retry {attempt+1} after {wait_time}s: {e}")
time.sleep(wait_time)
# Use with chain
try:
result = retry_with_backoff(lambda: chain.invoke({"question": "test"}))
except Exception as e:
result = "Service unavailable, please try again later."
# Fallback chain
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableWithFallbacks
primary_chain = prompt | ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o")
fallback_chain = prompt | ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
chain_with_fallback = primary_chain.with_fallbacks([fallback_chain])
result = chain_with_fallback.invoke({"question": "test"})
Tips: - Always set timeouts for production: with_config({"timeout": 30}) - Log errors with context for debugging - Use fallback chains for model unavailability
1.30 Multi-Query Retrieval
Brief: Generate multiple search queries for better recall.
Diagram:
┌──────────────────┐
│ Original Query: │
│ "LangChain uses" │
└────────┬─────────┘
│
↓ LLM generates variations
┌────────────────────────────────┐
│ Query 1: "How to use LangChain"│
│ Query 2: "LangChain usage" │──→ ┌───────────┐
│ Query 3: "LangChain examples" │ │ Retriever │
│ Query 4: "LangChain guide" │ └─────┬─────┘
└────────────────────────────────┘ │
↓
┌──────────────────────────┐
│ Doc1, Doc2, Doc3, Doc4 │
│ Doc2, Doc5, Doc6 │
│ Doc1, Doc7, Doc8 │
│ Doc3, Doc9, Doc10 │
└────────────┬─────────────┘
│ deduplicate
↓
┌──────────────────────────┐
│ Unique: Doc1-10 (merged) │
│ Better recall vs single │
└──────────────────────────┘
Code:
from langchain.retrievers.multi_query import MultiQueryRetriever
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
# Generates 3-5 variations of the query
multi_query_retriever = MultiQueryRetriever.from_llm(
retriever=retriever,
llm=llm
)
# Single query → multiple searches → deduplicated results
question = "What are the benefits of LangChain?"
docs = multi_query_retriever.invoke(question)
# Use in RAG chain
rag_chain = (
{"context": multi_query_retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
| prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
Tips: - Improves recall by 20-30% vs single query - Slower due to multiple retrievals (use caching) - Good for ambiguous or complex questions
1.31 Hybrid Retrieval (Dense + Sparse)
Brief: Combine semantic search (vectors) with keyword search (BM25) for best recall.
Diagram:
┌──────────────┐
│ User Query: │
│ "python RAG" │
└──────┬───────┘
│
├──────────────────────────────────┐
│ │
↓ Dense (Semantic) ↓ Sparse (Keyword)
┌──────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐
│ Embedding Model │ │ BM25 Algorithm │
│ "RAG concepts" │ │ Exact: "python" │
│ "retrieval apps" │ │ Exact: "RAG" │
└────────┬─────────┘ └────────┬─────────┘
│ │
↓ ↓
┌────────────────────┐ ┌────────────────────┐
│ Semantic Results: │ │ Keyword Results: │
│ Doc1 (score: 0.92) │ │ Doc3 (score: 8.5) │
│ Doc2 (score: 0.87) │ │ Doc1 (score: 7.2) │
│ Doc4 (score: 0.81) │ │ Doc5 (score: 6.8) │
└────────┬───────────┘ └────────┬───────────┘
│ │
└───────────┬───────────────────┘
↓ Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF)
┌───────────────────────────┐
│ Combined & Reranked: │
│ Doc1 (both methods) │
│ Doc3 (keyword strong) │
│ Doc2 (semantic strong) │
│ Doc4, Doc5... │
└───────────────────────────┘
Code:
from langchain.retrievers import EnsembleRetriever
from langchain_community.retrievers import BM25Retriever
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
# Setup documents
docs = [
"Python is great for RAG applications",
"LangChain simplifies retrieval-augmented generation",
"Vector databases store embeddings efficiently",
"BM25 is a keyword-based ranking algorithm"
]
# Dense retriever (semantic/vector)
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
vectorstore = FAISS.from_texts(docs, embeddings)
dense_retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 3})
# Sparse retriever (keyword/BM25)
sparse_retriever = BM25Retriever.from_texts(docs)
sparse_retriever.k = 3
# Hybrid: Combine both with weights
hybrid_retriever = EnsembleRetriever(
retrievers=[dense_retriever, sparse_retriever],
weights=[0.5, 0.5] # Equal weight, tune as needed
)
# Retrieves using both methods, merges results
results = hybrid_retriever.invoke("python RAG")
# Use in RAG chain
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
rag_chain = (
{"context": hybrid_retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
| prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
Tips: - Hybrid typically improves recall by 15-25% vs dense-only - Tune weights based on your data: [0.7, 0.3] for more semantic, [0.3, 0.7] for more keyword - BM25 excels at exact matches (product codes, names), vectors at concepts - For production, use Elasticsearch/Pinecone hybrid search endpoints (faster)
1.32 Contextual Compression
Brief: Compress retrieved documents to only relevant parts.
Diagram:
┌──────────┐ ┌───────────┐ ┌─────────────────────────┐
│ Question │→→│ Retriever │→→│ 10 Full Documents │
└──────────┘ └───────────┘ │ (1000 tokens each) │
└───────────┬─────────────┘
│
↓ Compressor LLM
┌───────────────────────────┐
│ Extract relevant snippets:│
│ Doc1: "...relevant..." │
│ Doc2: "...key part..." │
│ Doc3: "...answer..." │
└───────────┬───────────────┘
│ 50-80% reduction
↓
┌───────────────────────────┐
│ Compressed Context │
│ (200 tokens total) │
└───────────┬───────────────┘
│
↓
┌───────────────────────────┐
│ Final Answer (cheaper + │
│ more focused) │
└───────────────────────────┘
Code:
from langchain.retrievers import ContextualCompressionRetriever
from langchain.retrievers.document_compressors import LLMChainExtractor
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
base_retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 10})
# Extract only relevant parts from each doc
compressor = LLMChainExtractor.from_llm(llm)
compression_retriever = ContextualCompressionRetriever(
base_compressor=compressor,
base_retriever=base_retriever
)
# Retrieves 10 docs, compresses to relevant snippets
compressed_docs = compression_retriever.invoke("What is LCEL?")
# Use in RAG
rag_chain = (
{"context": compression_retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
| prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
Tips: - Reduces token usage by 50-80% (saves cost) - Improves answer quality by removing noise - Slower due to compression LLM calls
1.33 Streaming Responses
Brief: Stream tokens for better UX in chat applications.
Diagram:
Non-Streaming (Batch): Streaming (Token-by-Token):
┌────────────┐ ┌────────────┐
│ User waits │ │ User sees │
│ 5 seconds │ │ "The" │ 200ms
└──────┬─────┘ ├────────────┤
│ │ "The sky" │ 400ms
↓ ├────────────┤
┌────────────────────┐ │ "The sky │ 600ms
│ Full response: │ │ is blue" │
│ "The sky is blue │ └──────┬─────┘
│ because of Rayle- │ │
│ igh scattering." │ Better perceived speed!
└────────────────────┘
Flow:
┌──────────┐ ┌─────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ Prompt │→→│ LLM │→→│ Token 1 │→→│ Display │
└──────────┘ └────┬────┘ ├──────────┤ └──────────┘
│ │ Token 2 │→→
│ ├──────────┤
└───────→│ Token 3 │→→
└──────────┘
Code:
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
llm = ChatOpenAI(streaming=True)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are helpful."),
("user", "{question}")
])
chain = prompt | llm
# Stream tokens
for chunk in chain.stream({"question": "Explain quantum computing"}):
print(chunk.content, end="", flush=True)
# Async streaming
async for chunk in chain.astream({"question": "test"}):
print(chunk.content, end="", flush=True)
# With callbacks
from langchain.callbacks.streaming_stdout import StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler
llm = ChatOpenAI(
streaming=True,
callbacks=[StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler()]
)
Tips: - Essential for chat UX (perceived speed improvement) - Use astream_events() for granular control (tokens, tool calls) - Buffer partial responses for display
1.34 Function/Tool Calling
Brief: Let LLM call functions with structured arguments.
Diagram:
┌──────────────────────┐
│ User: "Weather in │
│ NYC and │
│ 12 * 15?" │
└──────────┬───────────┘
│
↓
┌──────────────────────┐ Available Tools:
│ LLM Decides: │ ┌─────────────────┐
│ │ │ get_weather() │
│ 1. get_weather(NYC) │←──│ calculate() │
│ 2. calculate(12*15) │ │ search() │
└──────────┬───────────┘ └─────────────────┘
│
↓
┌──────────────────────────────────┐
│ Execute Tools: │
│ ┌────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Tool 1: get_weather("NYC") │ │
│ │ Result: "Sunny, 72°F" │ │
│ └────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Tool 2: calculate("12*15") │ │
│ │ Result: 180 │ │
│ └────────────────────────────┘ │
└──────────────┬───────────────────┘
│
↓
┌──────────────────────────────────┐
│ LLM Synthesizes: │
│ "NYC weather is sunny and 72°F. │
│ 12 * 15 = 180" │
└──────────────────────────────────┘
Code:
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
@tool
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
"""Get current weather for a city."""
# In production, call actual API
return f"Weather in {city}: Sunny, 72°F"
@tool
def calculate(expression: str) -> float:
"""Evaluate a mathematical expression."""
return eval(expression)
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools([get_weather, calculate])
# LLM decides which tool to call
response = llm_with_tools.invoke("What's the weather in NYC?")
tool_calls = response.tool_calls
# Execute tool
if tool_calls:
tool_name = tool_calls[0]["name"]
tool_args = tool_calls[0]["args"]
if tool_name == "get_weather":
result = get_weather.invoke(tool_args)
# Or use agent for automatic execution
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_tool_calling_agent
agent = create_tool_calling_agent(llm, [get_weather, calculate], prompt)
executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=[get_weather, calculate])
result = executor.invoke({"input": "Weather in SF and calculate 15*23"})
Tips: - Use clear docstrings (LLM uses them for tool selection) - Add type hints for better argument parsing - Validate tool outputs before returning to user
1.35 Batch Processing
Brief: Process multiple inputs efficiently in parallel.
Diagram:
Sequential Processing: Batch Processing (max_concurrency=3):
┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ Input 1 │ 1s │ Input 1 │ │ Input 2 │ │ Input 3 │
├──────────┤ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘
│ Input 2 │ 1s Total: 5s │ │ │
├──────────┤ ─────────────────────────
│ Input 3 │ 1s │
├──────────┤ ↓
│ Input 4 │ 1s ┌────────────────┐
├──────────┤ │ Process batch │
│ Input 5 │ 1s │ concurrently │
└──────────┘ └───────┬────────┘
│
↓
┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ Input 4 │ │ Input 5 │
└────┬─────┘ └────┬─────┘
──────────────
│ Total: 2s (2.5x faster)
↓
┌─────────────────┐
│ All 5 Results │
└─────────────────┘
Code:
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
llm = ChatOpenAI()
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Translate to French."),
("user", "{text}")
])
chain = prompt | llm
# Batch invoke
inputs = [{"text": "hello"}, {"text": "goodbye"}, {"text": "thank you"}]
results = chain.batch(inputs)
# With concurrency limit
results = chain.batch(inputs, config={"max_concurrency": 5})
# Async batch
import asyncio
results = asyncio.run(chain.abatch(inputs))
# Stream multiple
for output in chain.batch(inputs):
print(output.content)
Tips: - Set max_concurrency to avoid rate limits (default: 4) - Use abatch() for better throughput with async - Batch size: 10-50 for optimal performance
1.36 Advanced Patterns (Reflection, ReAct, tools in graphs)
Brief: Improve reliability with self-critique, tool use, and ReAct.
Diagram:
┌─────────┐ ┌───────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐
│ Prompt │→→│ LLM Answer │→→│ Reflection │→→│ Final Output │
└─────────┘ └────┬──────┘ └────┬─────────┘ └────┬─────────┘
│ critique │ revise │ return
↓ ↓ ↓
Tool Calls ←─────────┘ (if needed)
Code (ReAct-style prompt sketch):
react_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Follow ReAct: Thought -> Action -> Observation."),
("user", "{input}")
])
react_chain = react_prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
Tips: - Add a reflection pass: LLM critiques its own answer before finalizing. - In graphs, model tool calls as nodes; capture observations in state. - Limit action space; enforce JSON for actions.
1.37 Best Practices
Brief: Guardrails, testing, logging, error handling.
Diagram (Streaming vs Batch):
Streaming: Batch:
┌────┐ tok tok tok → ┌──────────┐ ┌────┐ full response → ┌──────────┐
│LLM │──────────────→│ Client │ │LLM │────────────────→│ Client │
└────┘ └──────────┘ └────┘ └──────────┘
Tips: - Validate inputs/outputs; sanitize tool results. - Add retries with backoff for transient API errors. - Unit-test prompts/parsers; integration-test full chains. - Log prompts + responses securely (redact PII). - Monitor latency, cost, and error rates continuously. ```